7 - Advanced Text Generation Techniques and Tools
What can we do to further enhance the experience and output that we get from LLM without fine-tuning the model? There are several techniques that are available as shown in the figure below.
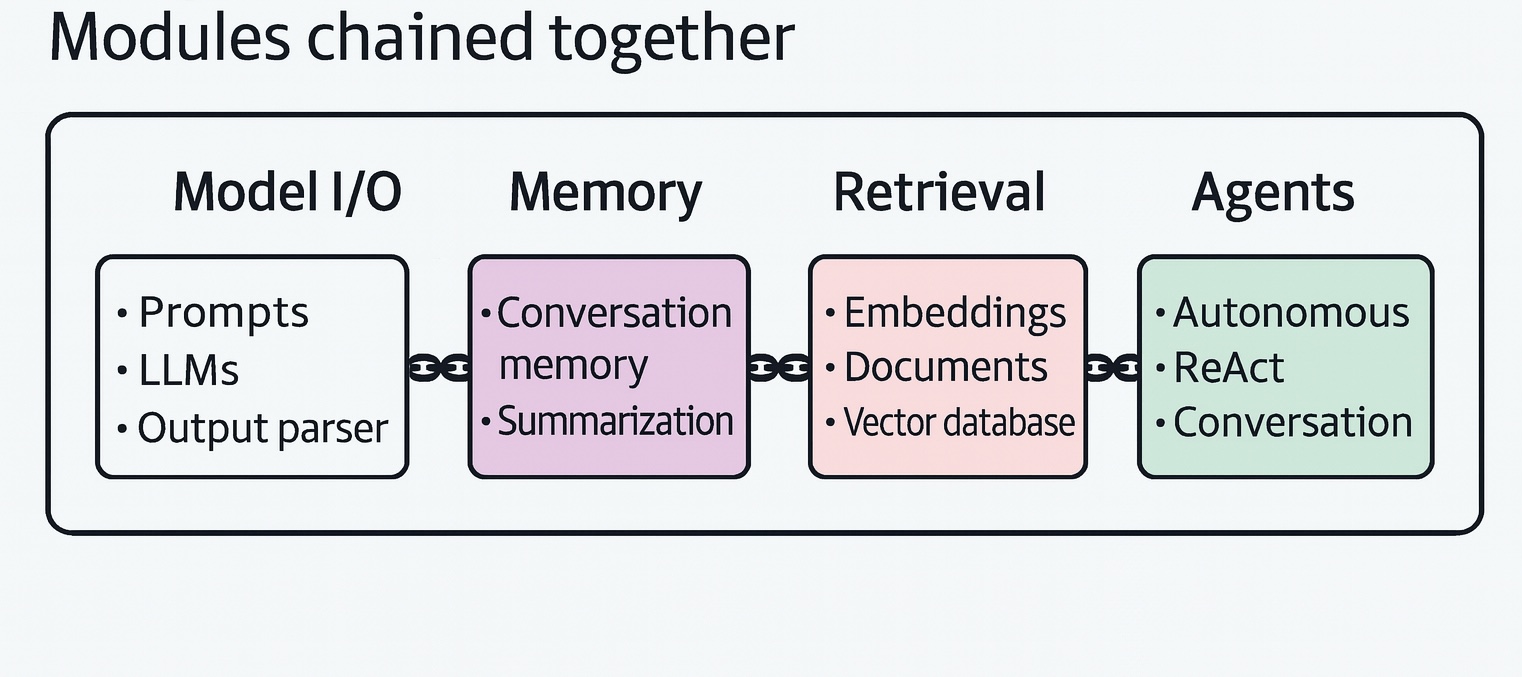
Model I/O
Loading Quantized Models with LangChain
Quantization is a method to compress the original model by reducing the precision of the values (e.g., 32-bit to 16-bit representation) without removing vital information. So it will be much faster to run the model with less VRAM.
Chains: Extending the Capabilities of LLMs
- By chaining prompt template to an LLM, we only need to define the input prompts, and the template will be constructed for you.
- When lengthy and complex prompts are required, we can break it into smaller sub-tasks to run sequentially, and it will require multiple calls to the LLM but with smaller prompts and intermediate outputs are available.
Memory: Helping LLMs to Remember Conversations
To make the models stateful with memory of previous conversations, we can add specific types of memory, more details in the summarization table below.
| Memory type | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversation Buffer | Copy the full conversation history and paste it into the prompt | - Easiest implementation - Ensures no information loss within context window | - Slower generation speed as more tokens are needed - Only suitable for large-context LLMs - Larger chat histories make information retrieval difficult |
| Windowed Conversation Buffer | Use the last k conversations instead of the full chat history | - Large-context LLMs are not needed unless chat history is large - No information loss over the last k interactions | - Only captures the last k interactions - No compression of the last k interactions |
| Conversation Summary | Summarize the entire conversation and distill it into the main points | - Captures the full history - Enables long conversations - Reduces tokens needed to capture full history | - An additional call is necessary for each interaction - Quality is reliant on the LLM’s summarization capabilities |
Agents: Creating a System of LLMs
Agents are systems that leverage a language model to determine which actions they should take with what order. They can use everything we’ve discussed so far such as model I/O, chains, memory, and can extend to two vital components:
- Tools that the agent can use to do things it couldn’t do itself (e.g., query internal DB)
- The agent type which plans the actions to take or tools to use
The driving force of many agent-based systmes is the use of a framework called Reasoning and Acting (ReAct), it combines two important concepts in behavior: reasoning and acting - it iteratively follows the three steps: thought, action, and observation.