3 - Looking Inside Large Language Models
An Overview of Transformer Models
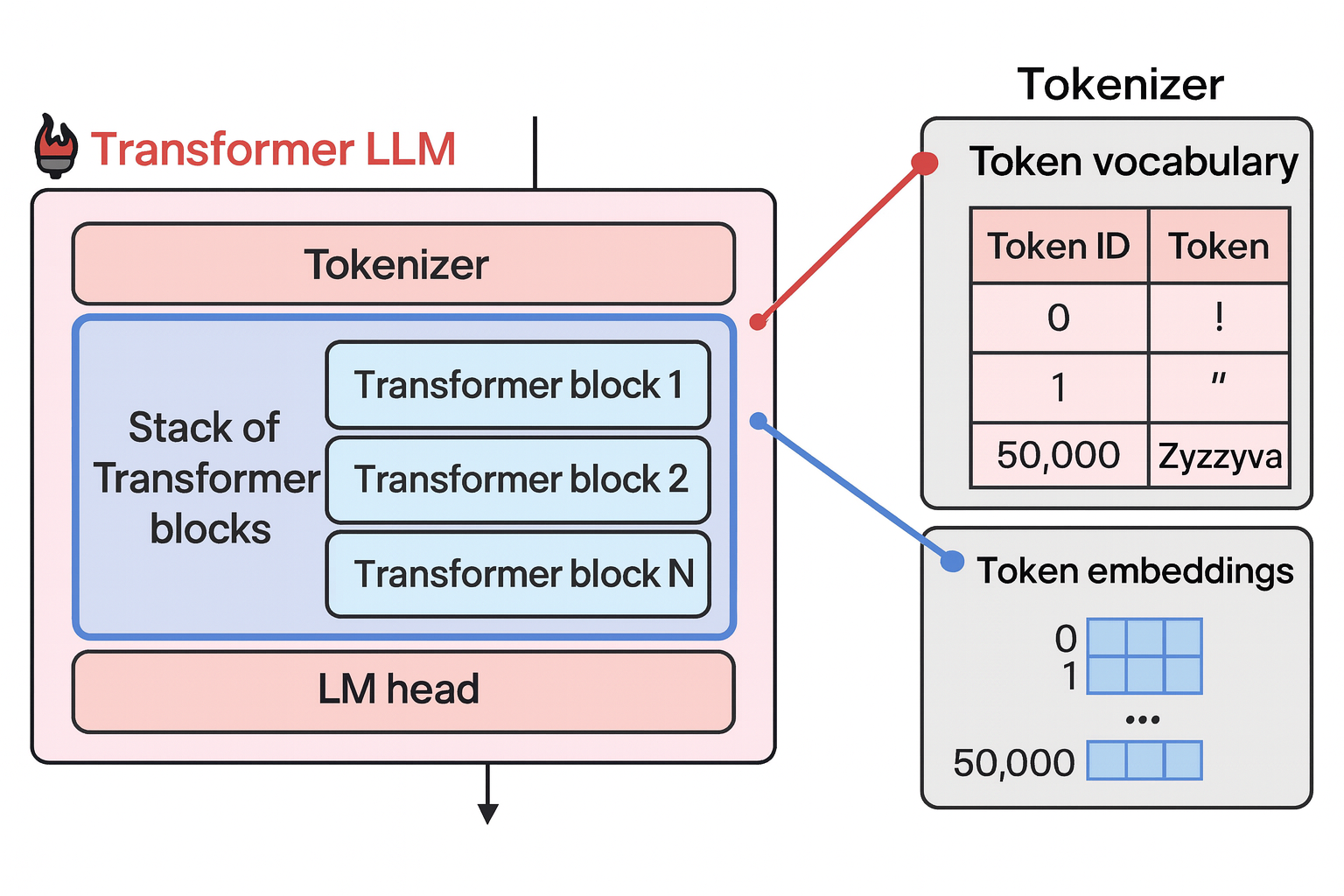
The Components of the Forward Pass
Tokenizer: breaks down text into a sequence of token IDs that becomes the input to the model
Transformer blocks: processes the input with the vector representations (embeddings) associated with each of the input token
Language modeling (LM) head: translate output into probability scores on what the most likely next token is. Done with a simple neural network layer
Choosing a Single Token from the Probability Distribution (Sampling/Decoding)
Greedy decoding: always pick the token with highest probability score - usually tend NOT to lead to the best outputs for most use cases
Sampling: add some randomness and sample from the probability distribution based on the probability score
Parallel Token Processing and Context Size
Parallel token: The tokenizer will break down the text into tokens, and each token flows through its own computation path.
Context size: the limit of how many tokens the transformer model can process at once.
Speeding Up Generation by Caching Keys and Values
Keys and values cache: Cache the results of the previous calculation (esp. the specific vectors in the attention mechanism), so we don’t need to repeat the calculations of the previous streams when generating the next token, and only need to calculate the last stream.
Inside the Transformer Block
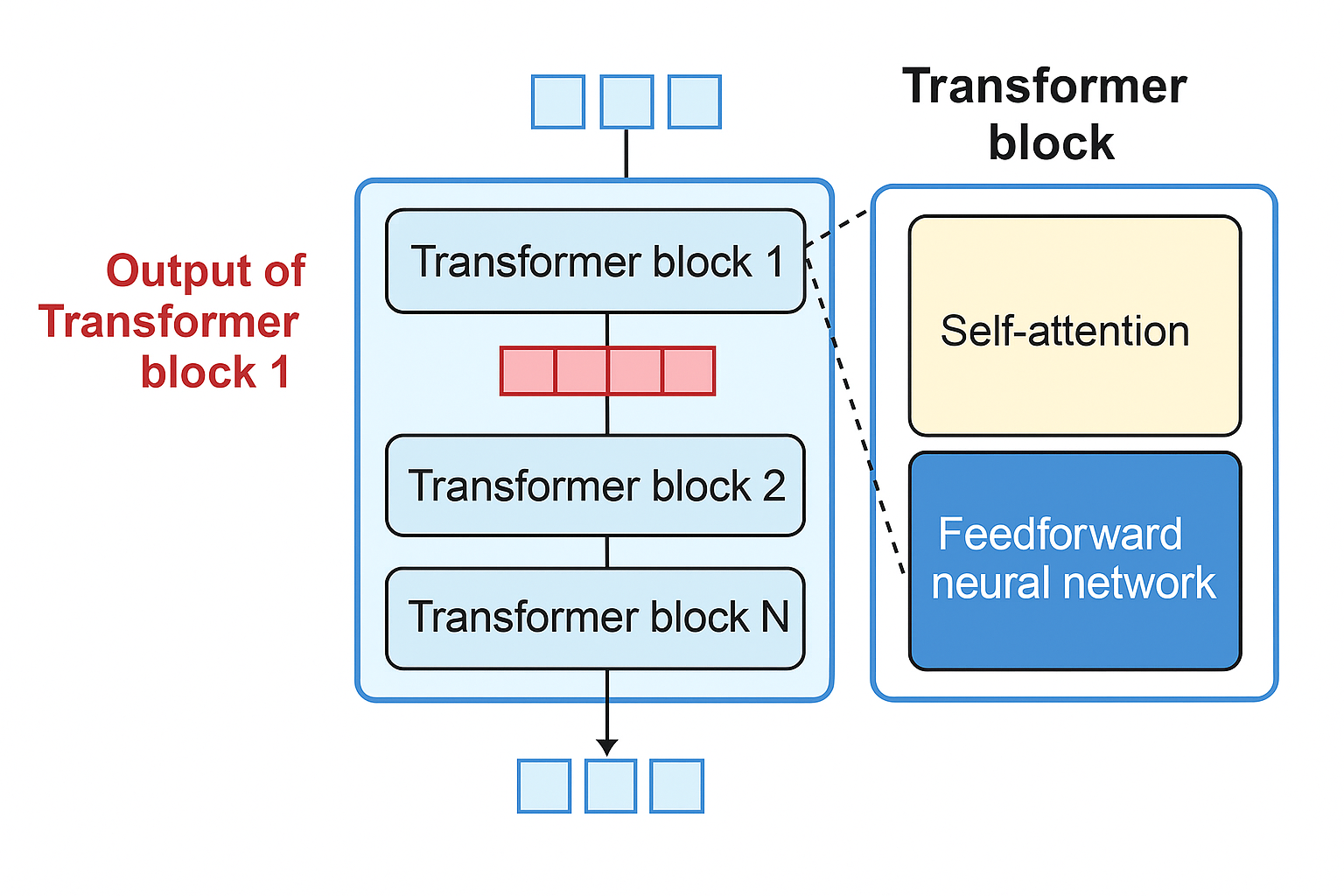
A transformer block has two successive components:
The attention layer: incorporate relevant info from other input tokens and positions
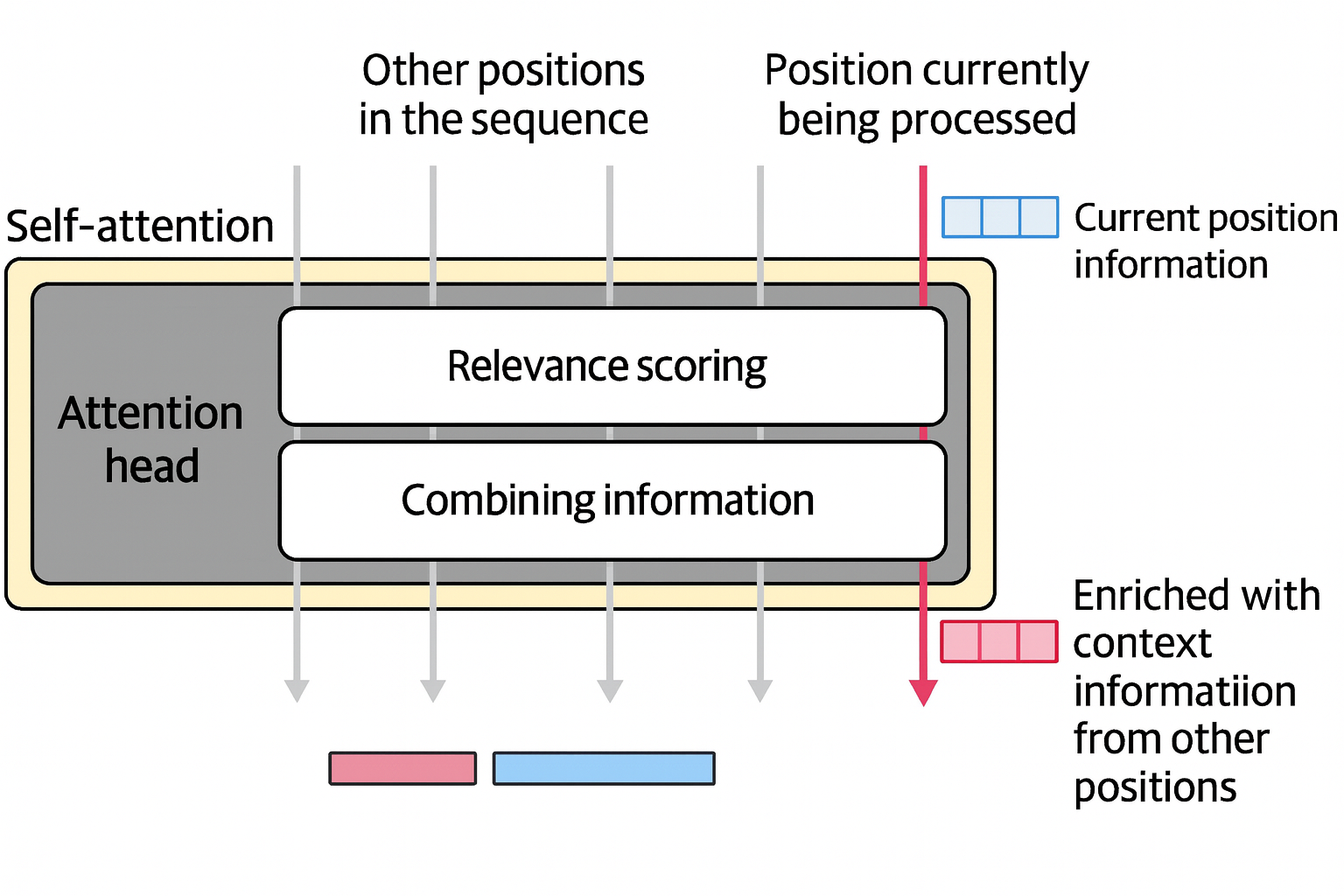
Attention is a mechanism that helps the model incorporate context as it’s processing a specific token.
Two steps in the attention mechanism:
- Relevance scoring of the previous input tokens to the current token
- Information combination of the various positions into a single output vector
The above attention mechanism is duplicated and executed multiple times in parallel in attention head to increase the model capacity to model complex patterns that require paying attention to different patterns at once.
The training process produces 3 projection matrices that produce the components that interact in this calculation: query, key, and value. (Qianqian: More details about this will be discussed in later blogs on attention).
The feedforward layer: the majority of the model processing capacity
- Intuition of feedforward NN: if we pass the simple input “The Shawshank” to the model, it is expected to generate “Redemption” as the most probable next word.
- During the training process, it learned and stored the info and behaviors that make it succeed at this task.
- In can both memorize and interpolate between data points and more complext patterns to be able to generalize on inputs it hadn’t seen before.
Recent Improvements to the Transformer Architecture
How to improve and create better models:
- Train on larger datasets
- Optimizations for the training process and learning reates to use
- The architecture improvements
- …
More Efficient Attention
- Local/sparse attention: limit the contexxt of previous tokens that the model can attend to
- Multi-query and group-query attention: share the keys and values matrices between all the heads (multi-query) or between the original multi-head and multi-query method to use different groups of keys and values (group-query) to improve inference scalability of larger models by reducing the size of the matrics involved
- Flash attention: optimize what values are loaded and moved between a GPU shared memory and high bandwidth memory
Improvement on Other Parts of The Transformer Block
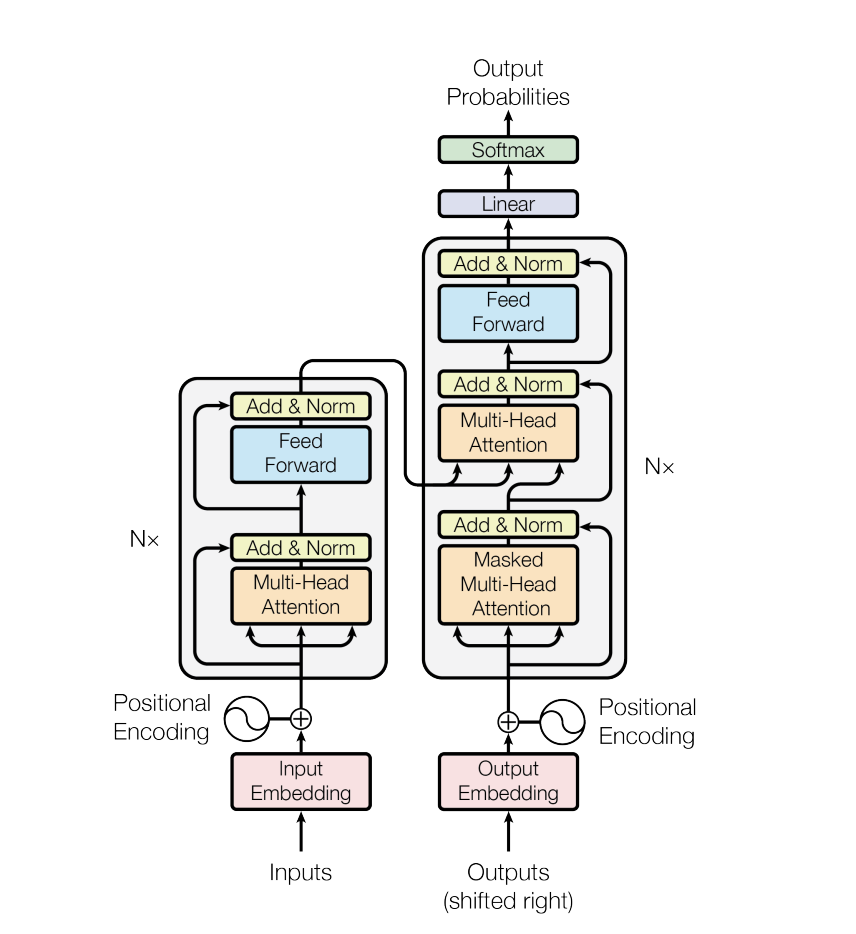
Other than the attention layer and feedforward neural network, the transformer block also has add and normalize as seen in the transformer block diagram from the original transformer paper. Improvements were made as follows:
- Normalization can happen before attention and feedfoward layers to reduce the training time.
- Can use RMSNorm, a simpler and more effieicnet way than LayerNorm in the original paper.
- Newer activation function variants such as SwiGLU than the ReLU activation function in the original paper.
Positional Embeddings (RoPE)
Use rotary positional embeddings instead of the absolte ones to encode positional info ina way that captures absolute and relative token position info.