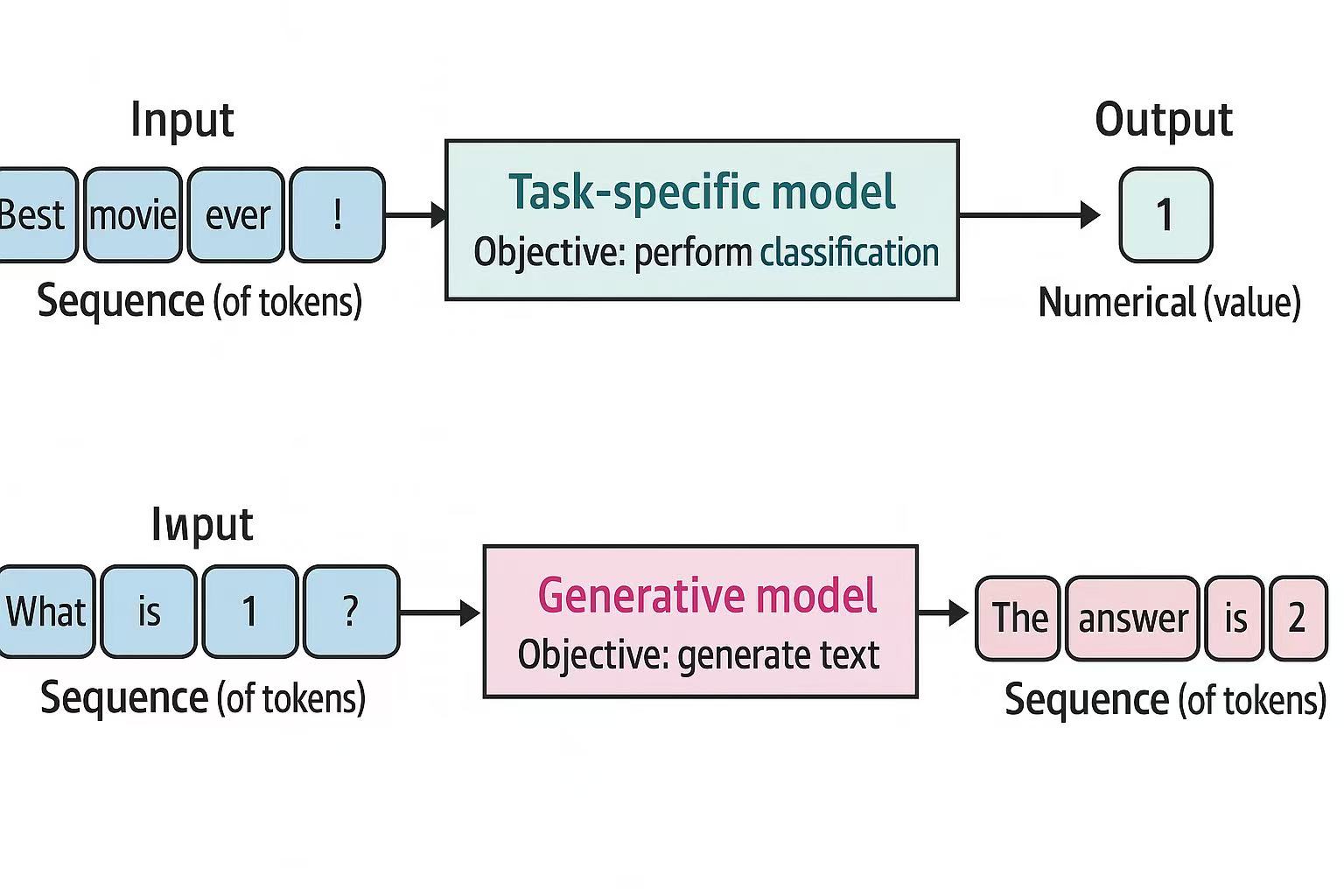
4 - Text Classification
Classifying text is used across a wide range of applications, from sentiment analysis and intent detection to extract entities and detect language. This chapter discusses different ways to use language models for classifying text such as using representation models or generative models.
Text Classification with Representation Models
Two types of classification with representation models based on fine-tuned foundation model:
- Task-specific model: a representation model trained for a specific task such as sentiment analysis.
- Embedding model: a representation model that generates general-purpose embeddings that can be used for a variety of tasks such as classification and semantic search.
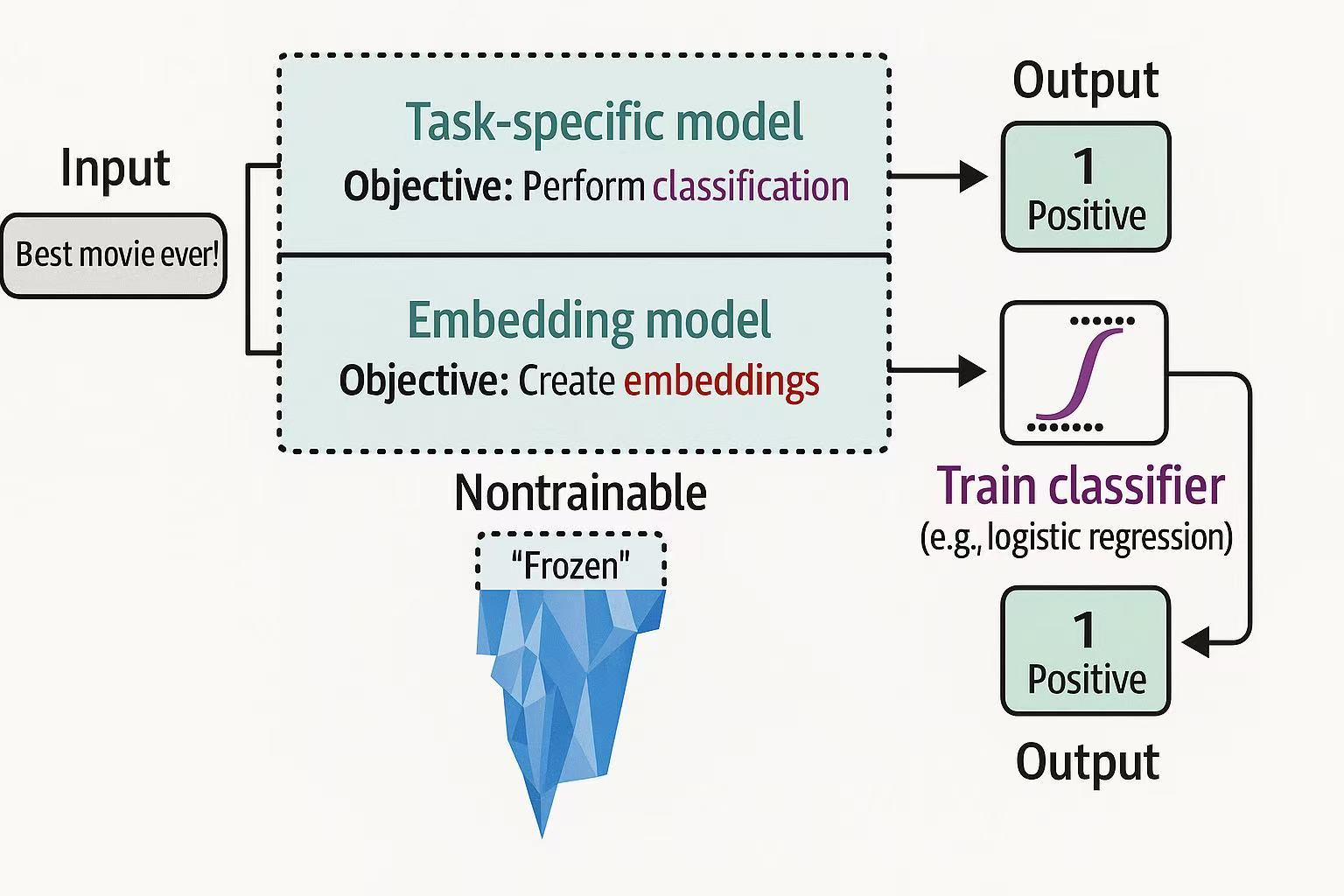
Model Selection
Factors that should take into consideration when selecting proper model:
- Choose the model that fits your use case
- Consider the language compatibility
- The underlying architecture: encoder-only (e.g., BERT) or decoder-only (e.g, GPT)
- Model size: encoder-only models tend to be smaller in size
- Performance
- Inference speed
Classification Tasks That Leverage Embeddings
Steps:
- Use embedding model to generate features
- Feed the features into a classifier for classification
What If We Do Not Have Labeled Data?
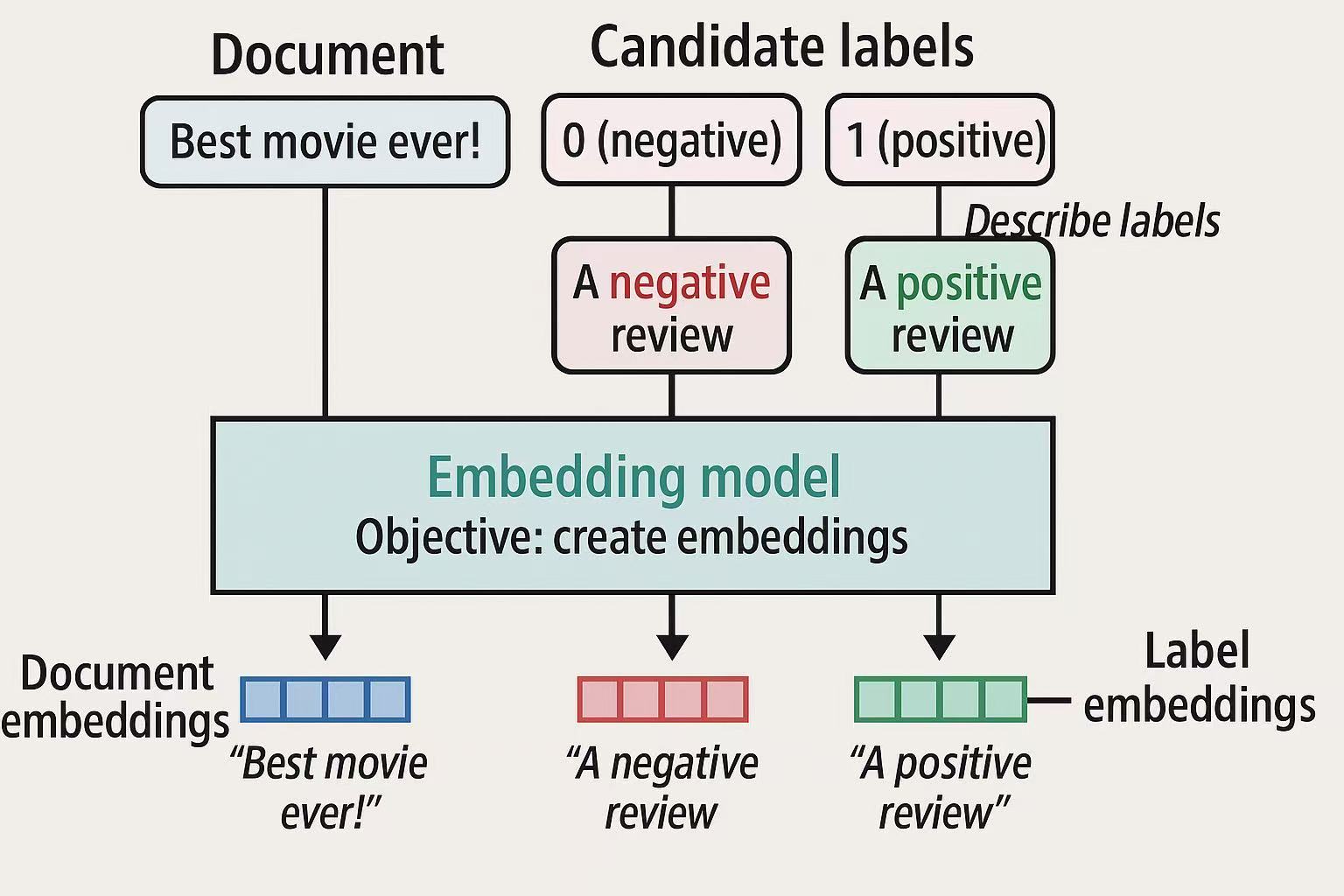
For cases when we have no labeled data, we can use zero-shot classification to predict the labels of the input text, and this will also help us to test if it is worthwhile to collect the labels, which is usually resource-intensive.
- Describe the labels based on what they should represent (e.g., a negative label for movie reviews can be described as “this is a negative movie review”)
- Create label embeddings based on the description (encoding)
- Assign labels to documents (input) by comparing the similarity between the document and the labed encodings
Text Classification with Generative Models
How is it different with the classification of the representation models? As shown in the diagram, a task-specific model (with representations) generate numerical values from tokens, while the generative model generates sequence of tokens that contain the classification results via prompt (or instruction) to guide the process.