Auto-complete based on N-Gram Model in Hadoop
Abstract
Build N-gram model with Hadoop based on texts data from Wiki, visualize real-time the auto-completion with JQuery, PHP, Ajax and SQL database.
Implementation of Auto-Complete with MapReduce
Overview
Visualization
The following pictures show screenshots of the visulization of autocomplte.
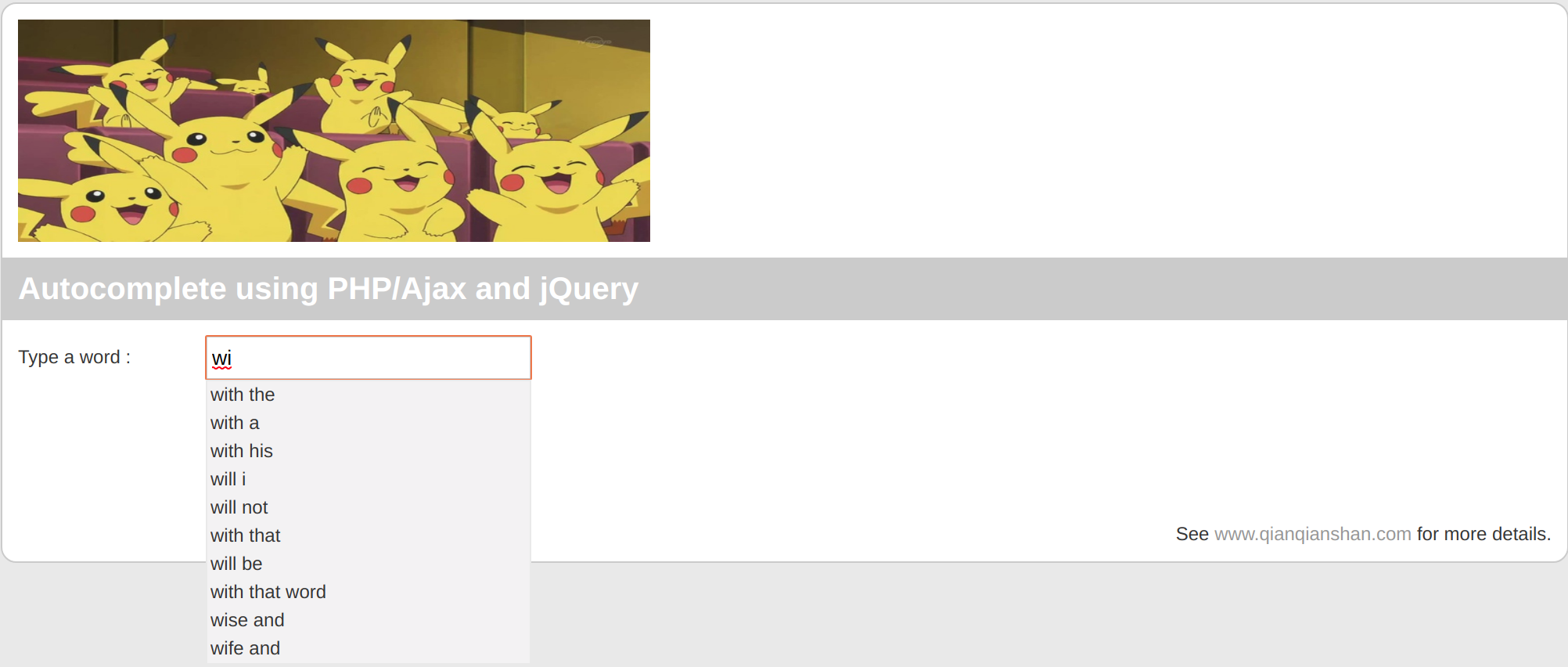
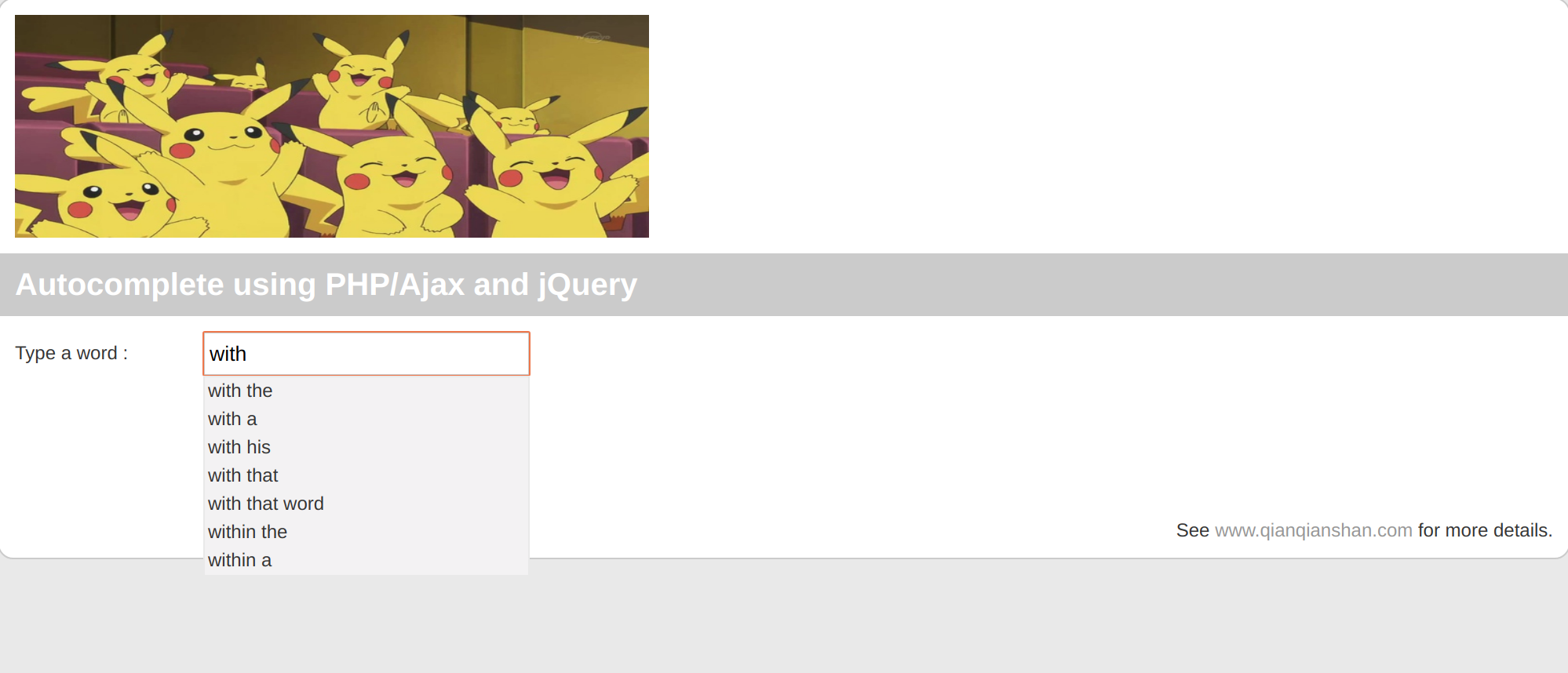
Visualization can be done using the files in autocomplete-visualization.tar:
cd /data/www/defaultin your local machine.wget --no-check-certificate https://github.com/QianqianShan/Auto_Complete/blob/master/autocomplete-visualization.tar, download the visualization files.tar -xvf autocomplete-visualization.tar, unzip the file, and there will be a folderautocomplete.cd autocomplete, in the following script segment ofajax_refresh.php, replaceyourpasswordwith your database password indefine ('DBPASS','yourpassword');andreturn new PDO('mysql:host=localhost;dbname=yourdatabasename', 'root', 'yourpassword', ..., also change thedbnameto your database name, for example I set my database name astestsodbname=test.
define ('DBUSER', 'root');
define ('DBPASS','yourpassword');
define ('DBNAME','test');
function connect() {
return new PDO('mysql:host=localhost;dbname=test', 'root', 'yourpassword', array(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE => PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION, PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_INIT_COMMAND => "SET NAMES utf8"));
}
Preliminaries
Operating system: The operating system is Ubuntu 18.04 LTS (Bionic Beaver).
Docker container (https://www.docker.com/why-docker) version 18.09.5:
Docker enables users to bundle an application together with its preferred execution environment to be executed on a target machine. (https://hadoop.apache.org/)
See https://docs.docker.com/install/ for more details on docker installation. Frequently used commands of docker can be found at https://docs.docker.com/get-started/.
- Hadoop cluster is launched within docker containers by following instructions at https://devhub.io/repos/joway-hadoop-cluster-docker, 3 containers with 1 master and 2 slaves will be started.
Output by running script start-container.sh:
start hadoop-master container...
start hadoop-slave1 container...
start hadoop-slave2 container...
- Visualize the auto-complete process with PHP, MySQL and jQuery as shown at http://www.bewebdeveloper.com/tutorial-about-autocomplete-using-php-mysql-and-jquery. LAMP (Linux, Apache HTTP server, MySQL, PHP) software bundle is used for the visulization (Wiki).
N-Gram Model
N-gram model is a language model which predicts the next word from the previous $(N-1)$ words, where N-grame is an N-token sequence of words such as “I like apple”(trigram), “New York”(bigram) and so on. The intuition of N-gram model is that we can approximate the probability of a word given the entire history by the probability given the last $(N-1)$ words.
Notation
Denote a sequence of $n$ words as $$ w_1^n=w_1,w_2,\cdots,w_n $$ and we have a computer-readable collection of text called corpus, $C$, that can be used to count frequencies of words or sequences. Denote the count of N-gram of words $$w_1,\cdots,w_N$$ as $$C(w_1,\cdots,w_N)$$.
Maximum Likelihood estimation (MLE) of Probability of Next Word
We obtain the MLE estimate of the probabilities of N-gram model by normalizing the counts from corpus $C$, that is, the ratio of counts of sequence
$$w_{n-N+1}^{n-1}w_n$$
over that of
$$w_{n-N+1}^{n-1}$$.
N-Gram Model Implementation
There are three main steps to implement N-gram model:
Calculate the counts of each n-gram for $n=1,2,\cdots,N$ based on raw data stored on hadoop distributed file systems (hdfs)
Calculate the counts of each following word given the previous word sequence and save the top $k$ frequent following words for each possible combination of previous word sequence into MySQL database.
Optimization of N-Gram Model in MapReduce
In the N-gram model, we predict the next word based on MLE of probabilities of words, this can be simplified by justing checking which word has the highest frequency to show up next given the previous $(N-1)$ words. For example, users input I like, and we have $$C(apple|I \quad like)=500$$ and $$C(banana|I \quad like) = 200$$ as the denominator $C(I like)$ is the same for the above two cases, the frequencies reflect their corresponding probabilities. Then we may want to recommend the trigram sequence as I like apple as first.
Discussion
N-gram model is sensitive to the corpus we are using. The probabilities are often an implication of specific facts of the used corpus.
N-gram model may assign some N-grams zero probability due to the limited corpus we are using. One can use smoothing methods to assign these kinds of N-grams non-zero probability, for example, Laplace smoothing, Good-Turing discounting and so on.
Run Auto-Complete in Hadoop
Set up LAMP
sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get -y install wget screen unzip, install wget, screen and unzip if not installed.screen -S lamp, run the installation process in background to avoid unexpected interruption.git clone https://github.com/teddysun/lamp.git, download lamp. See more details at https://github.com/teddysun/lamp.cd lampchmod +x *.sh, change script mode to executable../lamp.sh, install lamp.
Other installation options are shown at https://www.linode.com/docs/web-servers/lamp/install-lamp-stack-on-ubuntu-18-04/.
Set up MySQL
Create a database
CTL + ALT + Tto open a new terminalcd /usr/local/mysql/bin/sudo ./mysql -uroot -p, run as root password is also required to enter MySQL monitor, use the password you set up when installing LAMP.create database test;, create a database calledtest. Database can be dropped withdrop database test;use test;, switch to test databasecreate table output(starting_phrase VARCHAR(250), following_word VARCHAR(250), count INT);, create a table calledoutputwith three columns: starting_phrase, following_word, count. Table can be deleted withdrop table output;.GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;, grant MySQL remote login with thepasswordreplaced by the password of your MySQL server.SHOW VARIABLES WHERE Variable_name = 'port';check the port number to be used later.
Set up Hadoop in docker
./start-container.sh, start docker./start-hadoop.sh, start hadoopcd srcwget http://central.maven.org/maven2/mysql/mysql-connector-java/5.1.39/mysql-connector-java-5.1.39.jar, downloadmysql-connector-java-5.1.39-bin.jarfrom https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java/5.1.39 so we can write to local mysql after running MapReduce jobs.hdfs dfs -mkdir /mysql, create a foldermysqlin hdfs within hadoop.hdfs dfs -put mysql-connector-java-*.jar /mysql/, copy the previous downloadedmysql-connnector*.jartomysqlfolder of hdfs.wget --no-check-certificate https://github.com/QianqianShan/Auto_Complete/archive/v1.0.tar.gz, download source code and corpus.tar -xzvf v1.0.tar.gz, unzip the file, there will be a folderAuto_Complete-1.0.cd Auto_Complete-1.0.hdfs dfs -mkdir -p inputhdfs dfs -rm -r /output, if there exists an output folder.hdfs dfs -put bookList/* input/
Set up your IP, password and path to mysql connector in Driver.java:
1 - local_ip_address: can be found by
Method 1:
hostname -IMethod 2:
ifconfig | grep inet | grep broadcast
2 - MySQL_port:
SHOW VARIABLES WHERE Variable_name = 'port';check the port number to be used later.
3 - your_password: the password you set when you set up your MySQL database.
4 - hdfs_path_to_mysql-connector: for example, /root/src/mysql-connector-java-5.1.39.jar.
Run Auto-Complete
hadoop com.sun.tools.javac.Main *.javajar cf ngram.jar *.classhadoop jar ngram.jar Driver input /output 2 3 4,2 3 4are arguments passed to code, 2 is gram size, 3 is threshold size, 4 is following word size.Once the MapReduce job is done, use
select * from output limit 10;to check if your local database has been written with data.